Thursday, May 31, 2007
Week Twelve - Social & Ethical Issues 25/05/07
The internet has open protocols; anyone can publish, there is no control of unethical and bias information, and it has a lot of intelligent and unintelligent people. The problems on the internet are intellectual property, copyright, plagiarism, security, privacy and freedom of speech. Intellectual properties are ideas, inventions, movies and music. Plagiarism is copying others’ information without acknowledging the source. Security problems include probe attacks, virus contaminations, SPAM and spyware. Probe attack leads to content and password theft. Virus contamination is caused by opening email files, downloading files and peer to peer programs like MSN messenger.
Workshop
Film, video, multimedia and TV, and websites, internet, software and databases are relevant in my undergraduate course. Multimedia and software will be my main studies and I will have to follow the copyright laws carefully so I would not be plagiarising. In the US Dept of Justice Intellectual Property website it shows that US vs. Sankas was called operation buccaneer. For this cyber crime Warez leader was sentenced to 46 months of jail time. The leader of an internet software piracy establishment pleads guilty to the statements made to him.
The website about.com and pcmag.com links are not working properly so it is impossible to enter the specific page required. The only link that is working is http://www.howstuffswork.com/virus1.htm. To protect any computer from viruses is virus protection softwares, avoid unknown programs, purchase commercial software, use USB instead of floppy disks, have macro virus protection and never open email attachments that has executable programs.
Readings
The website History of Computer Viruses and the Open Architecture of the Internet by Shirlee-ann Knight is about early computer viruses, what are viruses, the first viruses (Brain, Lehigh, Jerusalem and Stoned), the first worms (Xerox Worms and Morris Worms), the internet and the spread of viruses and worms, ARPANET, internet protocols, recent and current viruses and threats, the types of viruses (file, macro, visual basic script and Trojan horses) and current viruses (Back Orifice, Chernobyl, BubbleBoy, Kakworm, Concept, Laroux, Melissa and Nimda).
The website Intellectual Property by Brown and Michaels is about utility, plant and design patents, trademarks, copyright, trade secret, computer softwares, domains and names.
The website EFF’s Top twelve ways to Protect your Online Privacy is about personal information, cookie management softwares, email addresses, personal details, advertisements, monitoring, SPAM, security, privacy and encryptions.
The website Email Attachments and Viruses is about risks of viruses.
The website Electronic Monitoring is about types of monitoring, privacy, legal issues, cases and policies.
The website Pro Music is about copyright, legal and illegal rights, personal use, uploading, file sharing and laws.
Summary
I went into the copyright website and read information related to my undergraduate course. Looked at the US Dept of Justice Intellectual Property website and read the articles on US vs. Sankas then I summarised it. Looked at websites that contain information on protecting computers from viruses. I wrote up a plan to protect computers from viruses and other unwanted softwares. And I summarised the readings for this week social and ethical issues.
Week Eleven: Building Knowledge 18/05/07

Lecture
Data is factual and non-judgemental. Information is relational, dimensional, permanent and has meaning. Knowledge is experiential, judgemental and very valuable. Collecting data must be valid and unbiased, quantity is better than quality and must be representable. Information must inform, the data must relate and must be meaningful. Knowledge is the justification of the data and information. Sampled data are like price, shares and exchange rates. Measured data are like weather and census data. Historical information is like almanacs and tables of census data. Records are like budgets and meetings.
Workshop
An online dictionary is very useful and a dictionary website called http://www.dictionary.reference.com/ may have helped some people in this week’s workshop. I looked up the term Data and received “a single piece of information, as a fact, statistic, or code; an item of data.” Information means “Knowledge derived from study, experience, or instruction.” And Knowledge means “The state or fact of knowing.” Understanding relationships will improve to the understanding of patterns then will improve the understanding of the principles.
Organisations collect information from their customers because the information helps them improve the quality of their services for the customers. Five organisations that do this are Telstra, Optus, Centrelink, Synergy and Alinta Gas.
Readings
The website Data, Information and Knowledge by Dr Jim Mullaney is about relationships and questions on building knowledge.
The website Data, Information, Knowledge and Wisdom by Gene Bellinger, Durval Castro and Anthony Mills is about data, information, knowledge, understanding and wisdom.
The website Information Literacy Tutorial by Thomas W. Eland is about production of knowledge, organisation of knowledge, thesis to search strategies, fundamentals of search engines, referencing resources, citing sources and copyright.
Summary
I used an online dictionary to find out terms of data, information and knowledge. I used Microsoft Words to draw a diagram of the data, information and knowledge. Wrote about the understanding the relationship between data, information and knowledge. I listed five organisations that collect information from people and explain why they do this. I summarised the readings for this week on building our knowledge.
Week Ten - Online Libraries & Databases 11/05/07
Lecture
Online libraries are convenient, can access many resources, journals are updated frequently, electronic formats are easy to make notes by copying and pasting, and can be accessed anytime anywhere. There are five types of online libraries which are online text repositories, online journals, electronic books, musical and artworks. The bad thing about online libraries is that often only the catalogue is online and this lets users browse and search the collections, a lot of libraries will require a fee to use its resources and the media item's quality may be reduced. Referencing online libraries is vital and has to be in APA format. Online databases are organised collections of information. They are similar to online libraries; it has search, browse, collecting and distribution tools. There are seven types of online databases which are people search, email directories, genealogy resources, maps and atlases, government information and statistics, news and media, and portals. The pros of online databases is that it is comprehensive, current, browsable, searchable, 24/7 access and it is in an electronic format. The cons of online databases are many databases is only accessible through subscription, there are lots of advertisements, navigation is difficult and there is too much information. Online libraries and databases are a very useful source of information, they are very similar, some cost money and some are free, and they are updated frquently.
Workshop
Ten useful things on the online library at ECU is the information about the ECU library, the resources for students, researchers and staff, referencing, multimedia resources, document delivery, loan services, catalogues, databases, websites and podcasts.
In the http://www.medlineplus.com/ there are 165 tutorials to choose from and I chose the Exercising for a Healthy Heart. Doctors, nurses, chemists and medical students may use this site to learn valuable information from it and they can get a lot of information from this site rather than having to search several other sites.
Summary
I looked around the ECU Online Library. Listed ten useful functions I have found on the Online Library. I entered the MEDline Plus website to look at health topics. I chose to pick Exercising for a Healthy Heart and searched for it in the website and then I did a tutorial on Exercising for a Healthy Heart. Then I wrote down who I thought would use this website and why they would use it.
Week Nine - Using Search Engines 04/05/07
There are two main types of search tools which are search engines and directories. Search engines are web based applications. They create indexes for websites and the searched results are indexed through keywords. Some types of search engines are Google, Yahoo!, AltaVista, AlltheWeb, Ask Jeeves, Excite, Turbo10, Lycos, Dogpile, Kartoo, MSN Search, HotBot, Teoma, Clusty, SearchEdu, Vivisimo, Web Wombat, Wisenut, Go Network and Zapmeta. The problem with search engines is the result because there is too many, some topics are not related to the searched keywords, includes broken links in the result list and incorrect information. Search engine interfaces display the URL links, a cached version of the websites and a link to similar pages to the web sites. There are four types of queries which are keyword, phrase, Boolean and advanced/engine features.
Workshop
Four strategies for a good search will be keyword searching, refining your search, relevancy ranking and Meta tags. Keyword searching is the most common way of searching on the web. Did a twenty questions quiz on http://www.siteseen.co.uk/ questions/generalknowledgehard/ which was about on getting information from search engines like google to answer the questions in the quiz.
I used a variety of search engines and they were Google, Yahoo!, AltaVista, AlltheWeb, Ask Jeeves, Excite, Turbo10, Lycos, Dogpile, Kartoo, MSN Search, HotBot, Teoma, Clusty, SearchEdu, Vivisimo, Web Wombat, Wisenut, Go Network and Zapmeta. They all have helped in the search for the correct answer in some way. Narrowing the information down is the most important because if the information is not narrowed down the result of the queried word might be too broad.
Readings
The website Internet Search Tips and Strategies by Robert Harris is about types of information on the internet like the visible web, the invisible web and paid web. The search tool types are search engines and directories. It tells us about keyword search, phrase search and Boolean operator.
The website Search Engine Tutorial by Danny Sullivan is about how to use search engines and it provides a guide on how to search resources on the web better.
The website Chapter Four: Search Engines by Richard T. Griffiths is about the history of the World Wide Web, finding information on the web, directories, search engines, databases and library catalogues.
The website the Spider’s Apprentice by Linda Barlow is about helping users understand and use search engines. The site tell users how it works, explains the results of the search, which search engine are the most useful and how to improve searches.
Summary
I listed four strategies on searching information on search engines. I completed the online quiz on researching the correct answer. Explained what search engines I used for this week workshop. Explained what I have learnt on this module. And summarised the readings for this week on using search engines.
Week Eight - Evaluation & Authentication 27/04/07
The World Wide Web is a fast and convenient way of exchanging information, anyone can create a website, and the World Wide Web can not be controlled by anyone. Who publishes relates to authorship, authority and authenticity. Why publishers publish relates to bias, accuracy and trustworthiness. What is published relates to currency, reliability and coverage. Anybody can create anything on the web. Often it is hard to find authorship on a web page. Qualifications and sponsorships are not usually given. Most of the goals of sponsors and authors on web pages are unclear. Publication dates may not be provided and if provided it may mean something else. Web information can be made up.
Workshop
To evaluate sources we have to find authority, accuracy, objectivity, currency, coverage and the value of the site. We would need to find who are the authors, who is in charge of it, what gives them the authority to write it, is there a good reason to believe it, what is the point of view of the authors, what purpose the site gives, are the dates on the website there and is it updated often. The Psychedelic ‘60s and the Sixties Project was a good source of information, it was worth visiting if someone is researching the 60s, I think the website is accurate, the facts are documented, the sites purpose and point of view tells us what happened in the 60s and these websites were designed for the web.
Readings
The website Thinking Critically about World Wide Web Resources by Esther Grassian is about the World Wide Web content, evaluating websites, sources, dates and structure.
The website Evaluating Internet Research Sources by Robert Harris is about evaluating information from websites and its quality. It tells us about credibility, author’s credentials, quality control, accuracy, time, comprehensiveness, audience, purpose, fairness, objectivity, moderateness, consistency, world view, support and corroboration.
The website Evaluation Criteria is by Susan about authority, accuracy, objectivity, currency and coverage.
The website Evaluating Information found on the Internet by Elizabeth E. Kirk is about authorship, publishing, point of views, bias, references, accuracy and currency.
The website Five Criteria for Evaluating Web pages by Jim Kapoun is about accuracy, authority, objectivity, currency and coverage of web documents.
Summary
Looked at ICYouSee website and read the critical thinking page. I summarised the strategies for evaluating information found on websites in my own words. Read all the articles on the 60’s on the same website. I chose two to evaluate to see if they are authentic. And I summarised all the readings for this week on evaluation and authentication.
Week Seven - Using the WWW 20/04/07
The web is like an imaginary space which contains an infinite amount of information, it exists because it allows computers to communicate with one another on the internet, without the web there could be no internet and the web made the internet useful to everyone. The web and internet was created by Tim Berners-Lee who was a researcher at CERN in 1989. He developed it to make sharing research information less difficult. The World Wide Web protocols are TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), DNS (Domain Name System) and URL (Uniform/Universal Resource Locator). DNS are www. (is in front of the URL), .com, .org, .net (are international domains), .au, .uk and .nz (are country codes). Com stands for commercial, org stands for organisation, net stands for network, gov stands for government and edu stands for education. To access the internet one needs a computer, a modem, a telephone line and an internet connection. Programs called web browsers allow users to explore the World Wide Web. The web browsers are Internet Explorer, MyIE2, Neoplanet, Netscape and Firefox. Web browser interfaces are very similar to one another like tools for searching and navigation tools. Shortcuts are used in web browsers to let users work faster without clicking on files to open or save something.
Workshop
The website http://www.haggishunt.scotsman.com/ is a broken link and can not be accessed. The website http://www.molossia.org/ appears to be authentic but it is not. The first page of the site has a phrase for the country but the phrase is a verse of a song someone has made and they just copied it. It gives an exact address of the place but it is a country so the whereabouts of this place is wrong. It gives fake information out which seems authentic but is not because they said ‘the Government of the Republic of Molossia takes no responsibility for the content of external links.’ And the beginning and ending of this country seems off because what kind of country only lives for thirty years. I expect the website www.martinlutherking.org to be about Martin Luther King and his history. The website is a non-profit organisation because org is at the end of the URL. It seems to be about the Martin Luther King but there are comments that say things that he did not do. The website Martin Luther King Organisation website is a biased site accusing Martin Luther King of horrible things that are untrue.
Readings
The website History of the Internet, Internet for Historians by Richard T. Griffiths is about the development of computers until the 1960’s, the history of ARPANET, the history of electronic mailing, search engines and basic net data.
The website a Little History of the World Wide Web by Dan Connolly is about fifty years of the World Wide Web from 1945 to 1995.
The website Search Engine Tutorial by Danny Sullivan is about how to use search engines and it provides a guide on how to search resources on the web better.
Summary
With a partner we looked at the http://www.molossia.org/ and http://www.martinlutherking.org/. We listed four clues that gave the Molossia site away as a fake site. Before we entered the website of Martin Luther King we guessed what the website was about. Then we read the Martin Luther King site and found out the site is a biased site created by racist people. And did three readings for this week about the World Wide Web.
Wednesday, April 18, 2007
Week 6: Using EndNote

Downloaded and installed the EndNote program to my computer.
Opened Microsoft Words and clicked on the EndNote icon to open program.
Read Workshop Supplemental EndNote References Exercises.
Put all references in EndNote put them in APA 5th style.
Screenshot the references and uploaded it in blogger.
Week 5: Information Management
Most of us use computers to manage our information.
Atom-based are hard copies of information. eg books, papers and reports. Pros - we can hold it, easy to protect and difficult to change and copy. Cons - size maybe a problem, costly and difficult to edit and distribute.
Bit-based are data information. They have an electronic content. Pros - file type can be changed easily to suite any format, it’s cheap, easy to edit, mass produce and broadcast. Cons - can easily be copied, SPAM, easy to steal, fake and changed.
The changed goods and services - internet banking, emails and mp3 players.
Changing goods and services - TV and shopping.
Newspapers, magazines and books are atoms which most of our information are received. Nicholas Negroponte told us a story which happened when he was visiting the headquarters of a circuit manufacturer in America and explained that his laptop (atom) was not worth much but the bits in his laptop was almost priceless. He told us another story where he visited a senior retreat where he presented samples of unreleased products (atoms) to the seniors to enhance their knowledge in communication technology. Soon after the samples were shipped back to the company but was checked in customs. On the same day he was sending data (bits) back and forth in cyberspace. His bits were not held up in customs unlike the atoms. In the internet weightless bits travels fast as the speed of light from one place to another to send and receive data. In the digital world advertisements and services of products is essential for any company who wants to enhance their company in the sales industry. But the products (atoms) will have to be move from one place to another place physically to transport the products to the consumers. A book is light weighted, easy to read through and not very expensive. But getting the book requires shipping and sometime books can go out of print then it will be impossible to buy one. Digital information can never go out of print, they are updated when new information is available, mostly free to view and they are always there.
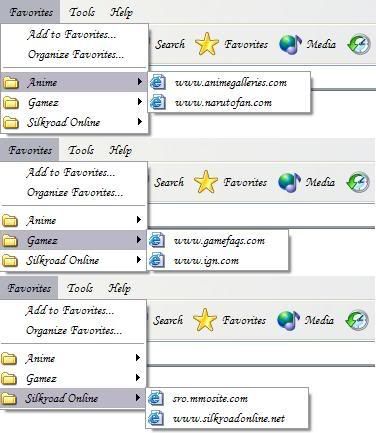
Read a tutorial on how to use bookmarks and favourites in the inette website.
I created 3 favourites folders (Anime, Gamez and Silkroad Online) with 2 websites in them each.
I took a screenshot of the favourite folders I did to upload in my blog.
Read Nicholas Negroponte’s ‘Being Digital’ ‘The DNA of Information.’
Then we wrote a 250 words review on ‘atoms’ and ‘bits.’
Week 4: Communications
There are networks for communications.
There are 4 types of communications. eg chat rooms, forums, MSN messenger and email.
Synchronous - Communicating at the same time. eg phone calls. (Same Time)
Asynchronous - Takes turns in communicating. eg emails. (Different Time)
“Place” Dependent - Have to be in same place to communicate. eg LAN games. (Same Place)
“Place” Independent - Can be anywhere to communicate. eg MSN messenger. (Different Place)
Some ICT’s are mobiles, videos, webcams, ipods, mp3 players, lap-tops, PDAs and emails.
Emails aren’t used for confrontation and complaining.
Emails are 1D and they can be forwarded to anyone to read.
Electronic journals and newsletters have a wide range of topics and subjects from academic journals to magazines, it’s updated frequently and is free most of the time.
Podcasts can be subscribed which allows new podcasts deliveries when they’re available, an abundant of broadcasters and topics to select from and they’re portable.
Forums are where people meet to discuss views and ideas, to inform them of news and announcements and to help each other with problems.
ICT’s are an invaluable source of information.
In Google in GROUPS, I entered ‘Naruto Shippuuden’ (anime). The groups it came up was in Arts and Entertainment, Computers - Games, Other and Recreation. The forums talked about the episodes that anime series was on, they discussed the characters in the anime and had links to sites related to the anime.
In http://podcasts.yahoo.com/ I entered ‘Naruto’ (anime) and listened to 2 podcasts. Then I looked around in http://podcast.osx.ecu.edu.au/index.html.
The potential benefits for university students from podcasting are being able to gain access to educational material at anytime and place that will help the student the most. It’s free most of the time and can be in a range of formats and it can be stored in mobile devices which could be used anywhere. Examples of some podcasts that helps students are recordings of lectures, tutorials, research, interviews and speeches.
Logged into ECU emails and created folders for each unit.
We sent an ECU email to a friend that was in the class.
We looked at forums in Google GROUPS.
We looked at podcasts in 2 podcasting websites.
Recorded what we did while we were in the forums and podcasts.
Week 3: Presentation Strategies


Audiences only remember 10% of seeing something, 25% of seeing and hearing, 40% of seeing, hearing and writing and 60% if they’re experiencing it interactively.
In a speech there is an introduction, body and conclusion.
There are 6 effective components to an introduction and 3 of them are ‘attention getters,’ thesis statement and preview.
The body should have the main ideas and references to research.
The conclusion should re-assert the thesis, revise the main ideas and close effectively.
Always keep a backup of your work.
Rehearse your speech.
For PowerPoint - KISS: Keep It Simple Stupid.
Only add things that will make the presentation better.
Ask the audience questions that will make the audience think.
Have good eye contact and speak clearly.
Read “How to give a bad talk” by David Patterson.
Read the notes we took from the lecture.
We created a PowerPoint presentation on how to make a good presentation.
I made 6 slides - title, introduction, 3 main bodies and a summary with an animation effect to enhance the presentation.
Screenshot all 6 slide to upload to my blog.
Week 2: Application Skills

How to use Windows Explorer, Microsoft Words, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint, Web Browsing and Adobe Acrobat Reader.
Listening, watching, viewing and editing media uses programs such as Windows Media Player, Winamp, RealPlayer, PhotoEditor, Paint and PhotoShop.
Opened the ‘Word Exercises’ document and read through it.
We used ‘Using Microsoft Word for APA Tasks’ to help us complete the ‘Word Exercises.’
We screenshot the document and edited it with Paint then uploaded it into our blogs.
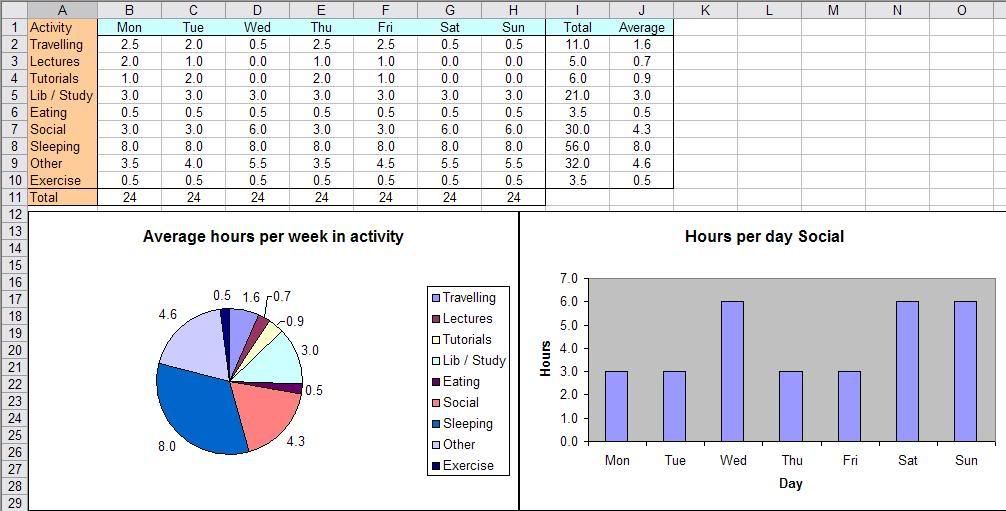
Opened the ‘Excel Exercises’ file and followed the instructions to complete the task.
We screenshot the document and edited it with Paint then uploaded it into our blogs.
Week 1: Introduction to Personal Computing
When we have completed this unit we’ll be able to access any material on the ECU website, produce documents at a university level and improve our teamwork skills in IT.
There will be 6 modules and 3 assignments for this unit.
We should attend all lectures and tutorials, complete all modules and assignments and check blackboard regularly.
The lecturers and tutors are Justine Freeman, Gary Chan and Alexa Krone.
Need thumb-drive
Logged into the ECU network and opened up to the ECU website.
Logged into ‘My ECU’ and accessed the unit resources and viewed Assignment 1.
We created an account in http://www.blogger.com/.
We created an account in http://www.imageshack.com/.
We screenshot and edited the screenshot in Paint or Photo Editor and saved it as a JPG.
